Predicting conversion to wet age-related macular degeneration using deep learning
18 May 2020
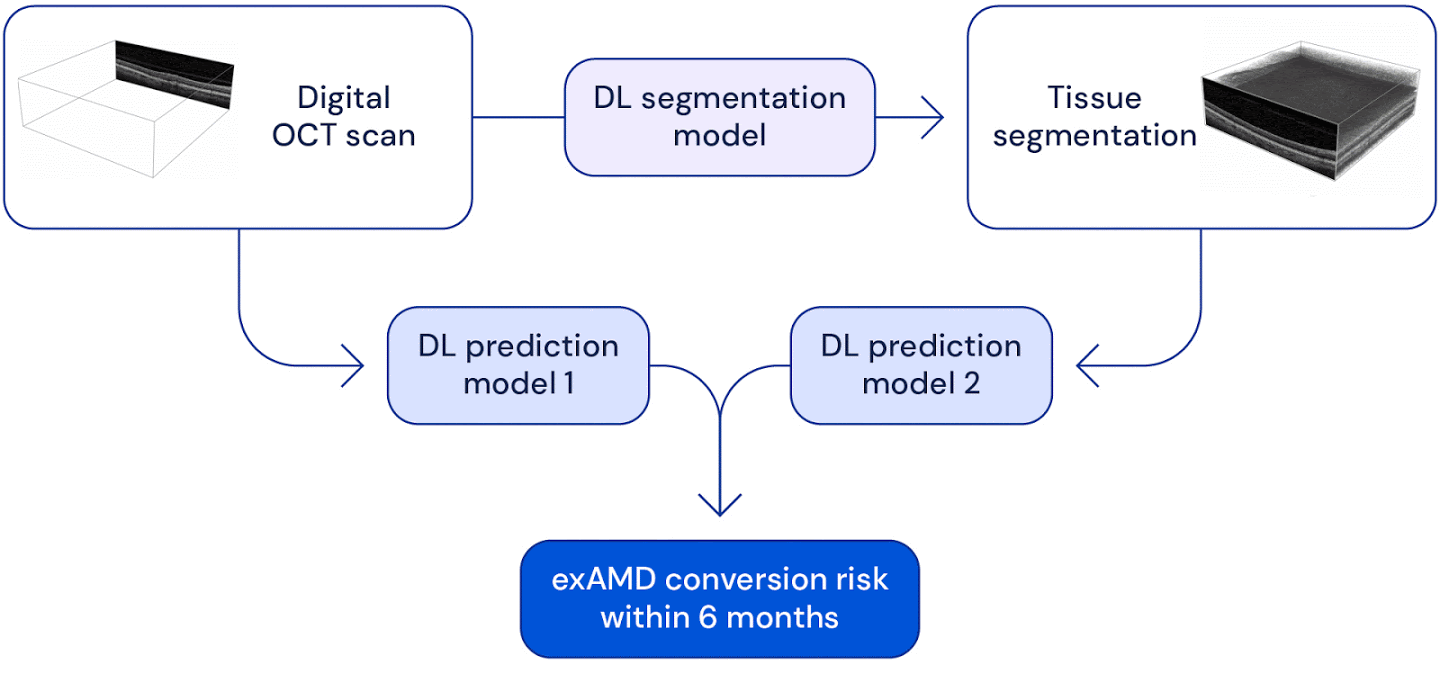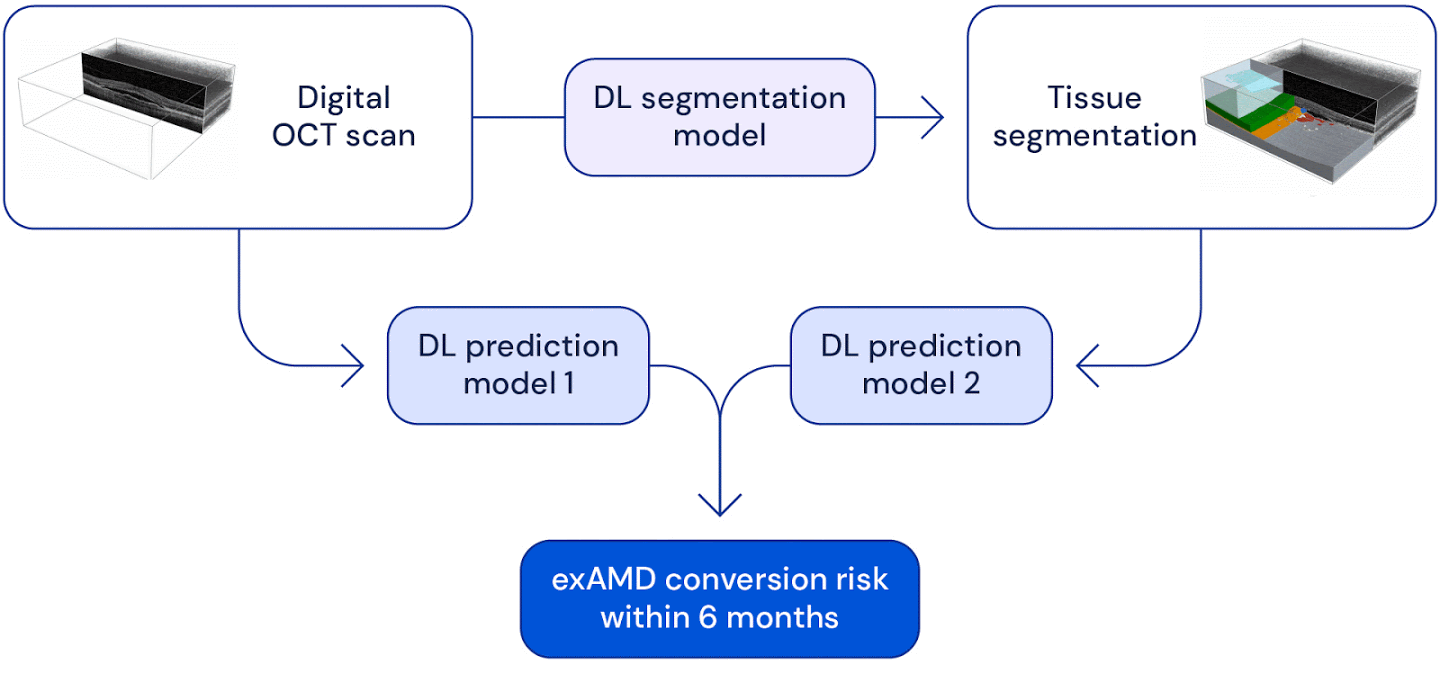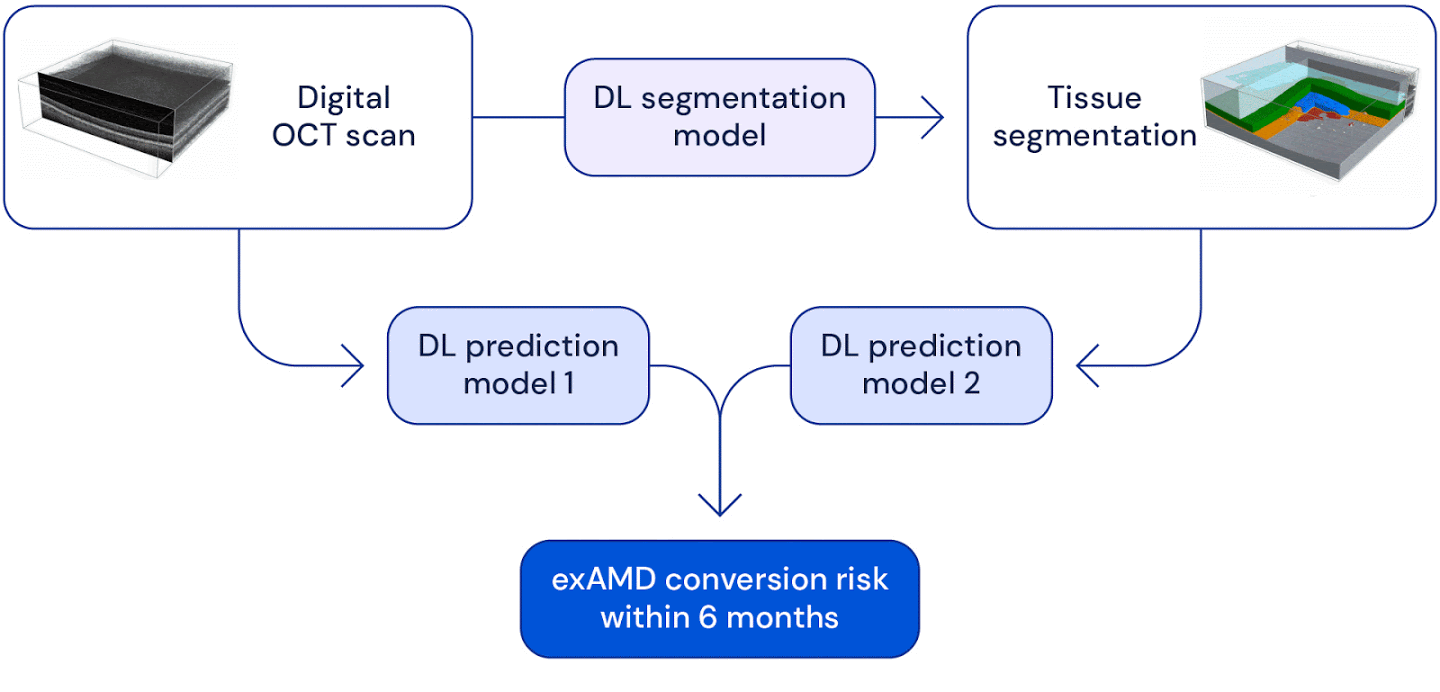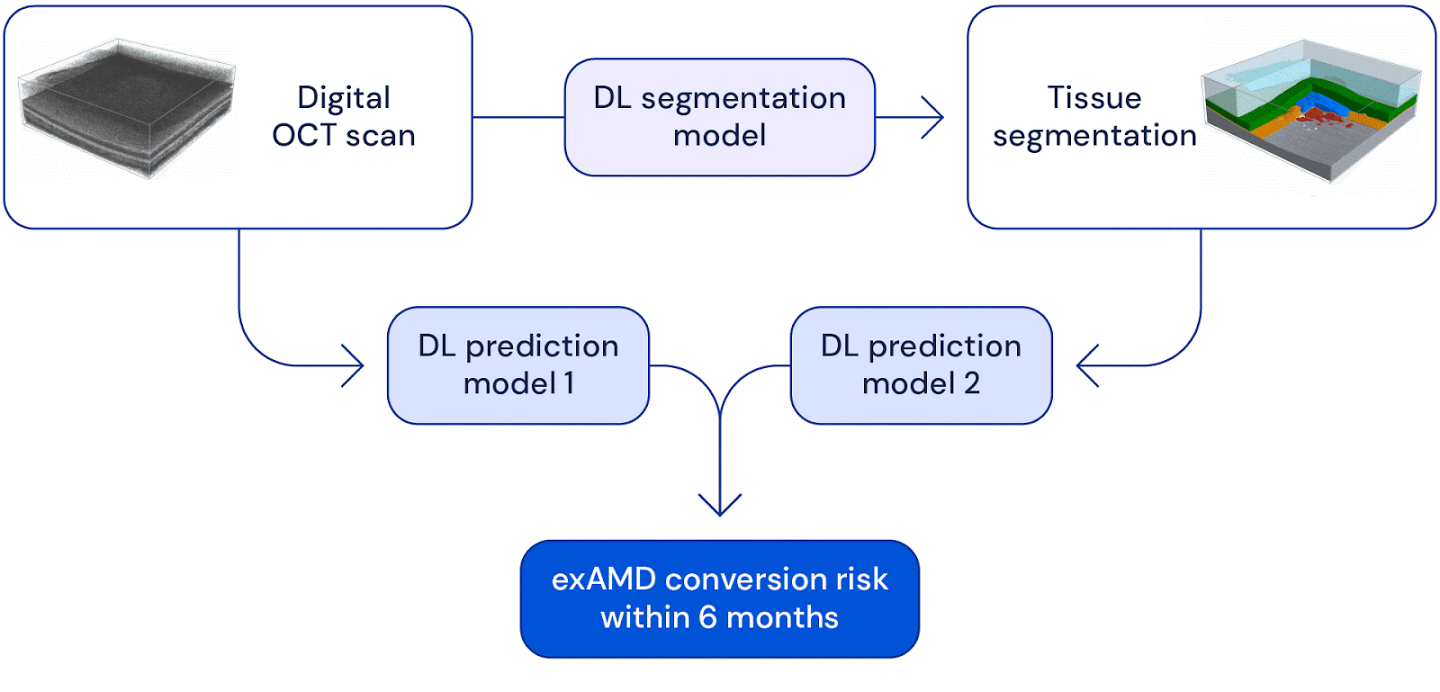
High level overview of the system used for wet AMD conversion prediction. We have two deep learning based models: one uses the original raw OCT scan to predict conversion, the other uses the the raw OCT segmented into several tissue types to predict conversion. Their predictions are ensembled to provide a single prediction of the risk to conversion within 6 months.
We look at predicting the progression of an eye to the sight-threatening form of AMD within 6 months. We demonstrate a deep learning system that is able to outperform five out of six experts on this task and importantly also overcomes the high interobserver variability from the experts.
Nature Medicine article
Open-access link
DeepMind blog post
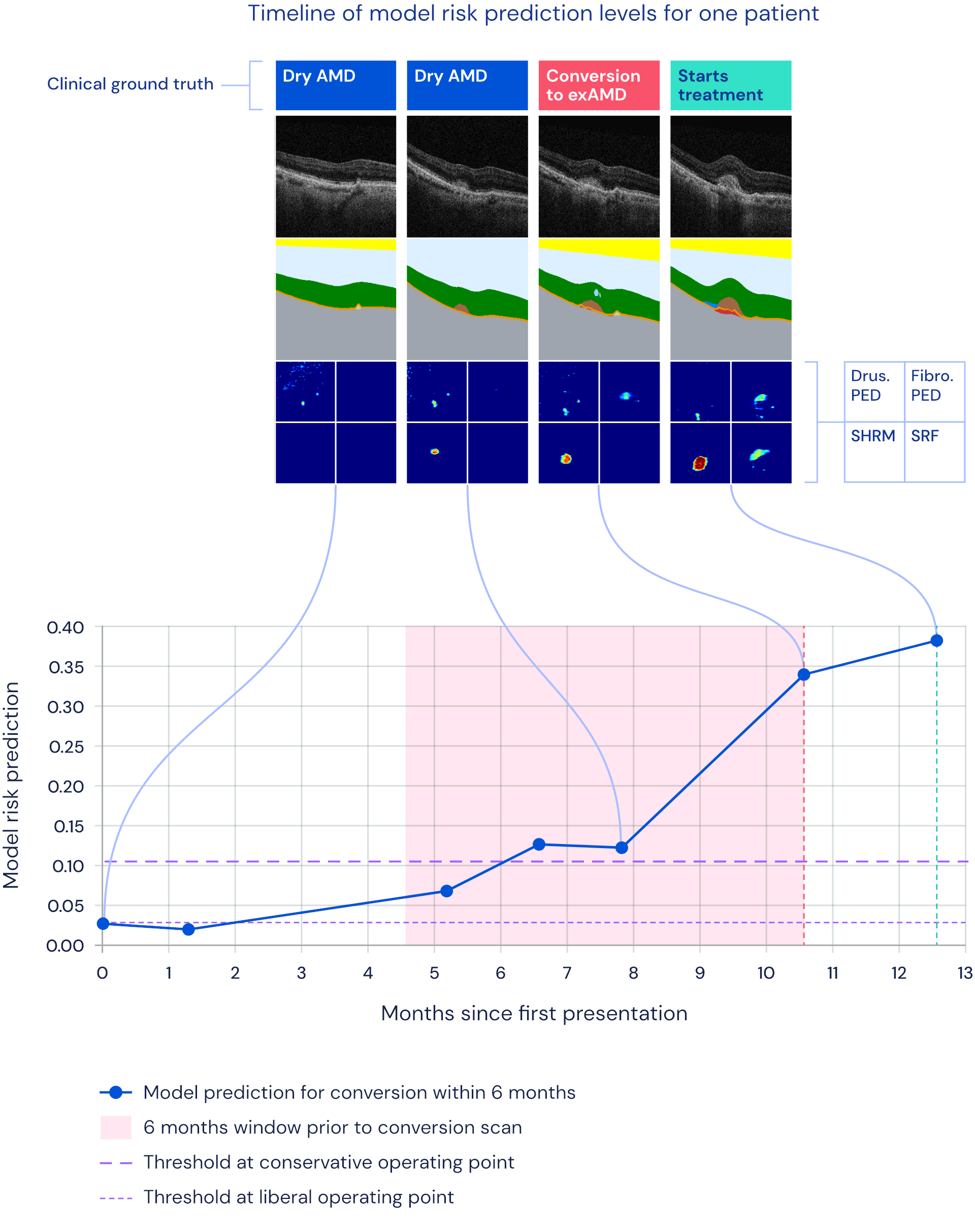
Timeline overview of an example patient's progression to wet AMD together with the model's risk prediction.
Jason Yim*, Reena Chopra*, Terry Spitz, Jim Winkens, Annette Obika, Christopher Kelly, Harry Askham, Marko Lukic, Josef Huemer, Katrin Fasler, Gabriella Moraes, Clemens Meyer, Marc Wilson, Jonathan Dixon, Cian Hughes, Geraint Rees, Peng T. Khaw, Alan Karthikesalingam, Dominic King, Demis Hassabis, Mustafa Suleyman, Trevor Back, Joseph R. Ledsam**, Pearse A. Keane** & Jeffrey De Fauw**
* equal contribution, order determined randomly
** jointly supervised the work
Abstract
Progression to exudative ‘wet’ age-related macular degeneration (exAMD) is a major cause of visual deterioration. In patients diagnosed with exAMD in one eye, we introduce an artificial intelligence (AI) system to predict progression to exAMD in the second eye. By combining models based on three-dimensional (3D) optical coherence tomography images and corresponding automatic tissue maps, our system predicts conversion to exAMD within a clinically actionable 6-month time window, achieving a per-volumetric-scan sensitivity of 80% at 55% specificity, and 34% sensitivity at 90% specificity. This level of performance corresponds to true positives in 78% and 41% of individual eyes, and false positives in 56% and 17% of individual eyes at the high sensitivity and high specificity points, respectively. Moreover, we show that automatic tissue segmentation can identify anatomical changes before conversion and high-risk subgroups. This AI system overcomes substantial interobserver variability in expert predictions, performing better than five out of six experts, and demonstrates the potential of using AI to predict disease progression.